About This Lesson
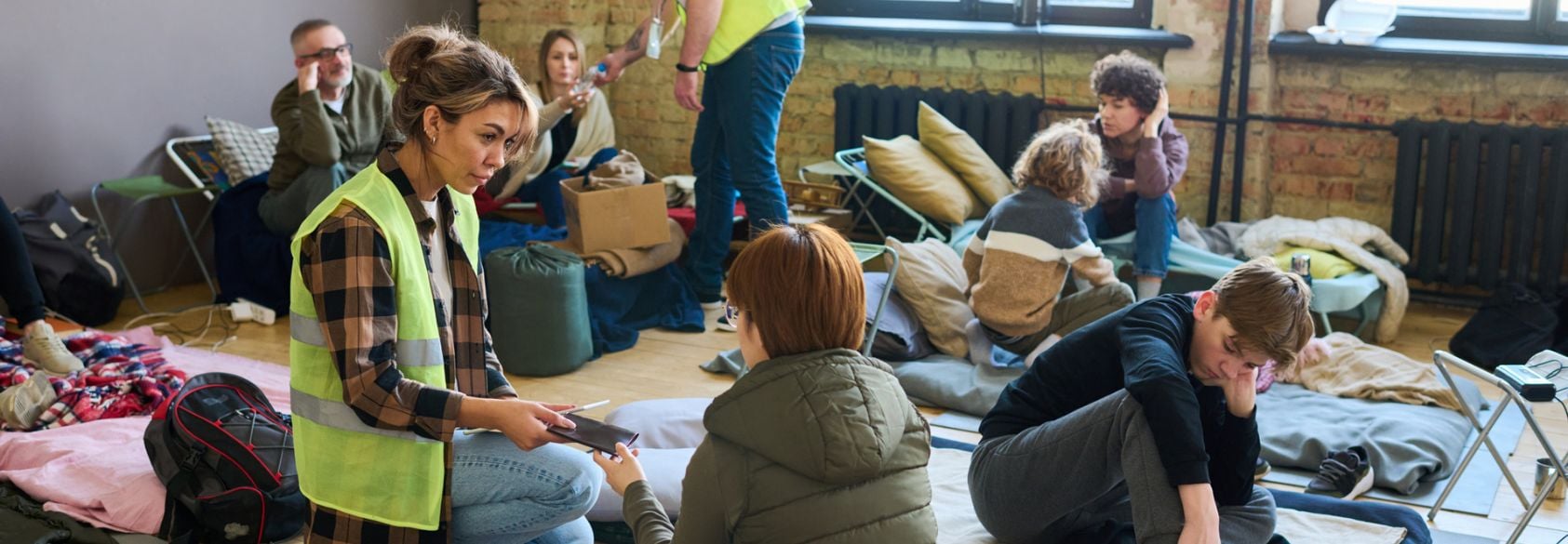
Hurricanes, flash floods, superstorms. Climate change is bringing more extreme weather, and the results can be catastrophic to our communities. As weather becomes more severe around the globe, there is an increased need for reusable shelters that can be easily transported and assembled to provide relief shelter for families who have been displaced from their homes.
In this activity, you will:
- Use design thinking to develop a lightweight, flat-folding, structurally-sound shelter for families displaced by natural disasters.
- Incorporate geometric shapes that add strength to structures in your design.
- Practice scaling up your design and converting between metric and U.S. customary systems of measurement.
Share your creations with Science Friday on Twitter or Facebook @SciFri- with the hashtag #DesignAShelter!
Teachers, you can find the full resource on Science Friday's website by clicking here.