About This Lesson
The lesson begins with students engaging in a whole-class review of range. Following the review, students participate in an activity designed to show them that the range may not be a useful measure of variation when a data set contains one or more outliers. Lesson objective: Students will be able to distinguish between measures of center and measures of variation and use interquartile range (IQR) as a measure of variation to describe data distributions. This is the fifth lesson of a seven lesson unit on statistics. Aligned with CCSS: 6.SP.2 , 6.SP.3








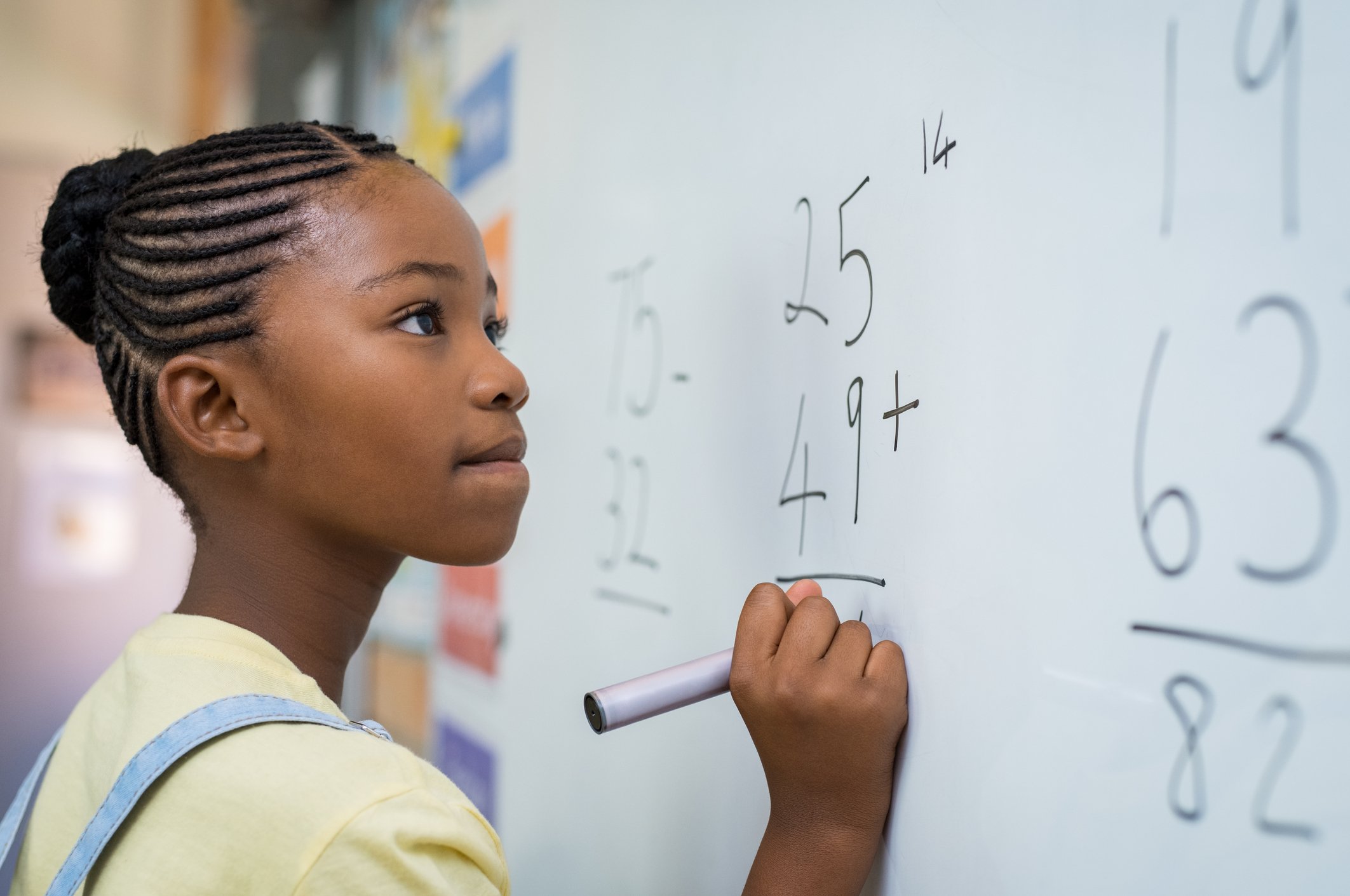

Very clear and organized lesson about quartiles with a variety of examples.