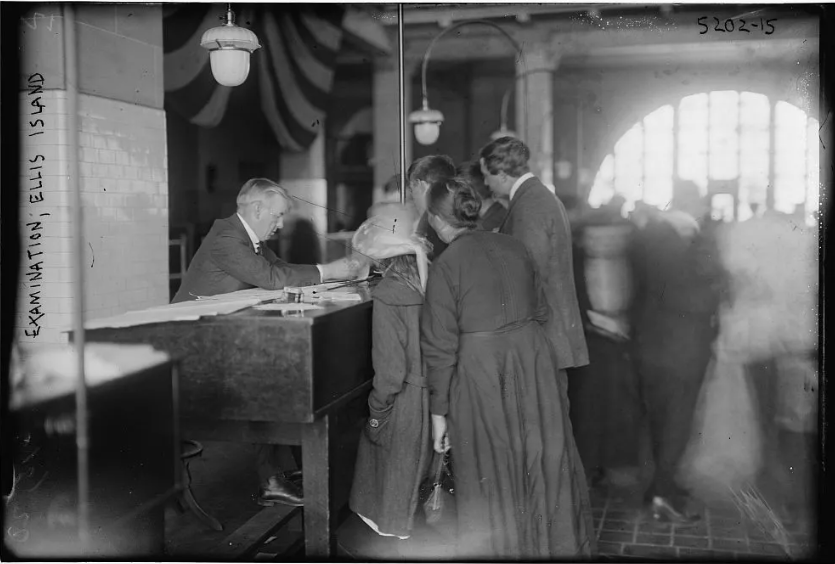
About This Lesson
Teaching Instructions:
- Read the article below to provide historical context for this lesson plan. You can create a PowerPoint presentation using the images and primary sources provided, or you can assign the reading to your students.
- Have students listen to the Ship History Radio podcast episodes or watch the films where Education Director Aimee Bachari interviews Dr. Kelli Nakamura about Asian and Japanese Immigration and the practice of Picture Brides. ** This interview touches on sensitive topics like racism, gender-based violence, child death, and prostitution. Listen first and assign with sensitivities in mind.**
- Have students answer the discussion questions in small groups or as a written assignment to be graded. If your students are working in groups, have them answer one question at a time and have groups share their responses with the larger class.
Rhode Island Social Studies Standards
- SSHS.CVC.3.4 Civil rights and civil liberties
- Argue the impacts of interpreting and using the Constitution of the United States to expand freedom and opportunity
- c. Analyze challenges to civil liberties (e.g., segregation, the internment of Japanese Americans, discrimination against people based on their race, ethnicity, gender, sexual identity), and argue their impacts
- Argue the impacts of interpreting and using the Constitution of the United States to expand freedom and opportunity
- SSHS.USI.5.5 Westward movement of white Americans
- Argue the impacts of western expansion on Indigenous peoples, immigration, and reshaping the United States
- b. Analyze the effects of the Gold Rush (e.g., on Indigenous peoples, on immigration of people from China, on the environment, on the economy), and argue who benefited
- Argue the impacts of western expansion on Indigenous peoples, immigration, and reshaping the United States
- SSHS.USII.1.4 Second-wave immigration to the United States
- Argue the influence industrialization had on second-wave immigration in the late 19th century, and the impacts of government responses
- a. Analyze the similarities and differences in the backgrounds, cultures, and lived experiences of U.S. immigrants after the Civil War (e.g., those from Italy, Poland, Russia, Portugal, Greece, Armenia, China, Japan, Korea, Punjab, Bengal, India, Mexico)
- b. Analyze the policies and practices of the U.S. government toward immigration (e.g., Chinese Exclusion Act 1882, Alien Land Act 1913, Immigration Act of 1924), and argue who benefited from those policies and practices
- c. Analyze the relationships among immigration, urbanization, and industrialization, and argue the impacts of those relationships
- d. Analyze the patterns of immigration and urbanization during the late 19th century, and explain the formations of ethnic neighborhoods in cities and their benefits
- Argue the influence industrialization had on second-wave immigration in the late 19th century, and the impacts of government responses
- SSHS.USII.4.1 Isolationism and the eventual involvement of the United States in World War II
- Analyze the United States’ attempts to remain isolated from global crises and the reasons for its eventual involvement in World War II
- d. Explain the conditions of and factors leading to the United States entering WWII (e.g., Pearl Harbor, German militarism)
- Analyze the United States’ attempts to remain isolated from global crises and the reasons for its eventual involvement in World War II
- SSHS.USII.4.2 The effects of the War on American society
- Argue how World War II impacted different groups of people in the United States
- e. Analyze the rationale for Japanese internment policies World War II, and argue the short and long-term impacts of those policies on Japanese communities
- Argue how World War II impacted different groups of people in the United States
- SSHS.WHII.4.3 Imperialism, expansion, and influence
- Argue how political and economic interests of western states impacted non-western territories in Asia and Africa
- b. Analyze the Meiji Restoration, how fear of western powers lead to it, and argue how it impacted the political and social structure of Japan
- Argue how political and economic interests of western states impacted non-western territories in Asia and Africa
Common Core Standards
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.9-10.2 – Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.11-12.1 – Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, connecting insights gained from specific details to an understanding of the text as a whole.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.11-12.2 – Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary that makes clear the relationships among the key details and ideas.